Past Research Projects
Mitigation of membrane fouling by control of microbial activity

Membrane fouling is often caused by biopolymers in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) process. Microbial quorum sensing is recently reported to associate with biopolymer production by sludge and consequent membrane fouling. We aim to specify the biopolymer components which majorly contribute to membrane fouling, and to reduce the components by inhibiting microbial activity including quorum sensing.
Resource recovery from wastewater by microalgae
Resource recovery from electronic waste by microalgae

Rare earth elements of Nd, Dy, Eu, Y are essential elements for electronic products like magnets, LED, etc. Recycling of rare earth elements is important for secured supply of these elements because only a few countries produce rare earth metals. Some microalgae have high adsorption capacity of rare earth elements. We investigate the optimum condition and mechanism of biosorption for recovery of rare earth metals from electronic wastes.
“Membrane Photobioreactor” process for microalgal biomass production

We developed a carbon dioxide capture process for global warming mitigation by intensive microalgae cultivation using nutrients in secondary treated sewage or leachate of anaerobic digestion process. Nitrogen and phosphorous in treated sewage causes eutrophication in lakes and semiclosed water bodies. However, their concentrations are still low to utlize them as media for microalgae cultivation. We invented a ‘Membrane Photobioreactor’ to realize a high-rate microalgae production in a low-nutrients medium, such as treated sewage. Installation of submerged membrane filtration in photobioreactor enables high loading of nutriens supply with treated sewage while maintaining a high concentration of microalgae.
Microalgae biomass produced from CO2 could be utilized as carbon-neutral bioenergy, such as biofuels by extracting lipids, methane gas by anaerobic digestion, solid fuel by carbonization, etc. We also focus on development of forward osmosis (FO) membrane process for concentration of nutrients in treated sewage to enhance microalgae productivity, and for simultaneous osmotic power generation.
Publications:
- Ryo Honda*, Jarungwit Boonnorat, Chart Chiemchaisri, Wilai Chiemchaisri, Kazuo Yamamoto (2012) Carbon dioxide capture and nutrients removal utilizing treated sewage by concentrated microalgae cultivation in a membrane photobioreactor. Biores. Technol. 125, 59-64. [Journal]
- Ryo Honda*, Yuta Teraoka, Mana Noguchi, Sen Yang (2017) Optimization of hydraulic retention time and biomass concentration in microalgae biomass production from treated sewage with a membrane photobioreactor. J. Water Environ. Technol. 15(1), 1-11. [Journal]
- Yasuhiro Furuhashi, Ryo Honda*, Hiroe Hara-Yamamura, Shoko Kobayashi, Koichi Higashimine, Hiroshi Hasegawa (2019) Optimum conditions of pH, temperature and preculture for biosorption of europium by microalgae Acutodesmus acuminatus. Biochem. Eng. J. 143, 58-64. [Journal]
FO membrane process for concentration of treated sewage and microalgae biomass

Forward osmosis (FO) membrane process enables energy-saving concentration of a solution by osmotic pressure difference. We aim to develop processes to concentrate nitrogen and phosphorus to improve productivity of microalgae in a membrane photobioreactor process and produced microalgae biomass. We collaborated with University of California, Los Angeles on this topic.
Publications:
- Ryo Honda*, Weerapong Rukapan, Hitomi Komura, Yuta Teraoka, Mana Noguchi, Eric M.V. Hoek (2015) Effects of membrane orientation on fouling characteristics of forward osmosis membrane in concentration of microalgae culture. Biores. Technol. 197, 429-433. [Journal]
- Weerapong Rukapan, Ryo Honda, Ryo Yoshizawa, Eric M.V. Hoek (2014) Impacts of pH on Concentration of Nitrogen and Phosphorus using Forward Osmosis Membrane. Proceedings of The 7th International Young Water Professional Conference, Taipei, December 7-11, 2014.
Production of building block chemicals for biorefinery from treated sewage

Microalgae were utilized to produce starch from carbon dioxide and nutrients in treated sewage. The intracellular starch can be converted to building blocks for biorefinery, e.g. bioplastics production, etc. We investigated the optimum conditions to maximize starch productivity from treated sewage, and conversion of intracellular starch in HMF, a builiding block of epoxy resin.
Publications:
- April Htet, Mana Noguchi, Kazuaki Ninomiya*, Yota Tsuge, Kosuke Kuroda, Shinya Kajita, Eiji Masai, Yoshihiro Katayama, Kazuhiro Shikinaka, Yuichiro Otsuka, Masaya Nakamura, Ryo Honda, Kenji Takahashi (2018) Application of microalgae hydrolysate as a fermentation medium for microbial production of 2-pyrone 4,6-dicarboxylic acid. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 125(6), 717-722. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2017.12.026
- Sen Yang, Yoshiki Hakumura, Mana Noguchi, Ryo Honda (2015) Starch Production Process from Treated Sewage by Microalgae Cultivation in a Membrane Photobioreactor. Proceedings of 1st IWA Resource Recovery Conference: Bridging towards the chemical industry, Ghent, August 30 – September 2, 2015.
Anaerobic Photosynthetic Process for organic wastewater treatment and biomass production

A wastewater treatment process utilizing purple non-sulfur bacteria (PNSB) was developed aiming conversion of organics in wastewater into cell biomass. Optimization of wastewater feeding for selective growth of PNSB in a mixed culture condition and introduction of membrane separation for stabilization of treatment were studied. Recent topics are on optimization of lighting in a scaled-up reactor and microbial flora analysis. This study is conducted in collaboration with Kasetsart University, Thailand.
Publications:
- S. Chitapornpan, C. Chiemchaisri*, W. Chiemchaisri, R. Honda, K. Yamamoto (2013) Organic carbon recovery and photosynthetic bacteria population in an anaerobic membrane photo-bioreactor treating food processing wastewater. Biores. Technol. 141, 65-74. [Journal]
- S. Chitapornpan, C. Chiemchaisri*, W. Chiemchaisri, R. Honda, K. Yamamoto (2013) Organic carbon recovery and photosynthetic bacteria population in an anaerobic membrane photo-bioreactor treating food processing wastewater. Biores. Technol. 141, 65-74. [Journal]
- Ryo Honda*, Kensuke Fukushi, Kazuo Yamamoto (2006) Optimization of wastewater feeding for single-cell protein production in an anaerobic wastewater treatment process utilizing purple non-sulfur bacteria in mixed culture condition. J. Biotechnol. 125(4), 565-573. [Journal]
Reduction of greenhouse gases emission by unutilized resources in sewage treatment plants
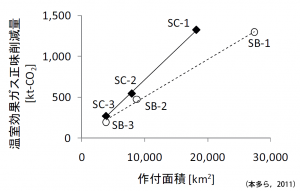
Greenhouse gases emission from sewage system corresponded to approximately 0.5% of total emission in Japan in 2004. Reduction of GHG emission was estimated based on various scenarios to utilize available ground in sewage treatment plants for introduction of solar cells and wind power generation at available sites in sewage treatment plant and sewage sludge for fuel crop cultivation.
Publications:
- Ryo Honda and Kensuke Fukushi (2011) Potential of greenhouse gases reduction by fuel crop cultivation utilizing sewage sludge in Japan. Environ. Syst. Res. 39, II_299-305. (in Japanese) [Abstract]
Ryo Honda and Kensuke Fukushi (2011) Potential of energy generation by introduction of photovoltaic and small wind power system in sewage treatment plants in Japan. J. Japan Soc. Civil Eng. G. 67(2), 47-53. (in Japanese) [Abstract]
Resource flow between urban and agricultural sectors in peri-urban area in Asia
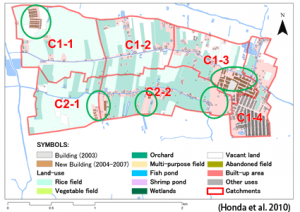
Expansion of Bangkok Metropolitan causes sprawl housing development in peri-urban agriculture area. Wastewater from newly developed houses were discharged without sufficient treatment into creeks which still utilized as an agricultural water resource. Cycle flow of nutrients mediated by canals were analyzed in Nonthaburi Province, which locates in peri-urban Bangkok. Change of nutrients load into the canals was estimated based on land-use analysis in the target survey area. A housing development scenario with low GHG emission was proposed by interdisciplinary collaborating work with experts on landscape ecology, solid waste management, human ecology and agricultural economy.
Publications:
- R. Honda*, Y. Hara, M. Sekiyama and A. Hiramatsu (2010) Impacts of housing development on nutrients flow along canals in a peri-urban area of Bangkok, Thailand. Water Sci. Technol. 61(4), 1073-1080. [Journal]
- Yuji Hara*, Ai Hiramatsu, Ryo Honda, Makiko Sekiyama, Hirotaka Matsuda (2010) Mixed land-use planning on the periphery of large Asian cities: the case of Nonthaburi Province, Thailand. Sustain. Sci. 5(2), 237-248. [Journal]
- Ai Hiramatsu*, Yuji Hara, Makiko Sekiyama, Ryo Honda (2009) Municipal solid waste flow and waste generation characteristics in an urban-rural fringe area in Thailand. Waste Management Res. 27(10), 951-960. [Journal]
Sustainability assessment on water resources utilization
Use of water does not always result in decrease of water. Most of water usage is for flushing and washing, which may deteriorate quality but cause little change in supplied and discharged amount. Moreover, now water is a renewable resource as wastewater is available even as a drinking water resources due to development of membrane technology. Water shortage can be defined as ‘quantitative shortage’, which caused by imbalance in amount of resources and withdrawal, or ‘qualitative shortage’, which caused by increase of cost in treatment of polluted resources. Shift of water withdrawal assoiated with change of cost in water use was studied based on economical analysis. Sustainability indices for water resources were proposed including qualitative evaluation of water resources.
Publications:
- Ryo Honda, Hirotaka Matsuda (2010) Conceptual development of sustainability assessment for water resources. WateR-InTro Workshop on Research and Development for Water Reuse Technology in Tropical Regions 2010, Phuket, Thailand, October 2010.
